-
 1
1
-
 2
2
-
 3
3
-
 4
4
-
 5
5
-
 6
6
-
 7
7
-
 8
8
-
 9
9
-
 10
10
-
 11
11
-
 12
12
-
 13
13
-
 14
14
-
 15
15
-
 16
16
-
 17
17
-
 18
18
-
 19
19
-
 20
20
-
 21
21
-
 22
22
-
 23
23
-
 24
24
-
 25
25
-
 26
26
-
 27
27
-
 28
28
-
 29
29
-
 30
30
-
 31
31
-
 32
32
-
 33
33
-
 34
34
-
 35
35
-
 36
36
-
 37
37
-
 38
38
-
 39
39
-
 40
40
-
 41
41
-
 42
42
-
 43
43
-
 44
44
-
 45
45
-
 46
46
-
 47
47
-
 48
48
-
 49
49
-
 50
50
-
 51
51
-
 52
52
-
 53
53
-
 54
54
-
 55
55
-
 56
56
-
 57
57
-
 58
58
-
 59
59
-
 60
60
-
 61
61
-
 62
62
-
 63
63
-
 64
64
-
 65
65
-
 66
66
-
 67
67
-
 68
68
-
 69
69
-
 70
70
-
 71
71
-
 72
72
-
 73
73
-
 74
74
-
 75
75
-
 76
76
-
 77
77
-
 78
78
-
 79
79
-
 80
80
-
 81
81
-
 82
82
-
 83
83
-
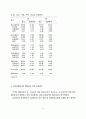 84
84
-
 85
85
-
 86
86
-
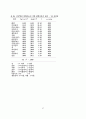 87
87
-
 88
88
-
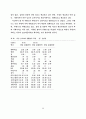 89
89
-
 90
90
-
 91
91
-
 92
92
-
 93
93
-
 94
94
-
 95
95
-
 96
96
-
 97
97
-
 98
98
-
 99
99
-
 100
100
-
 101
101
-
 102
102
-
 103
103
-
 104
104
-
 105
105
-
 106
106
-
 107
107
-
 108
108
-
 109
109
-
 110
110
-
 111
111
-
 112
112
-
 113
113
-
 114
114
-
 115
115
-
 116
116
-
 117
117
-
 118
118
-
 119
119
-
 120
120
-
 121
121
-
 122
122
-
 123
123
-
 124
124
-
 125
125
-
 126
126
-
 127
127
-
 128
128
-
 129
129
-
 130
130
-
 131
131
-
 132
132
-
 133
133
-
 134
134
-
 135
135
-
 136
136
-
 137
137
-
 138
138
-
 139
139
-
 140
140
-
 141
141
-
 142
142
-
 143
143
-
 144
144
-
 145
145
-
 146
146
-
 147
147
-
 148
148
-
 149
149
-
 150
150
-
 151
151
-
 152
152
-
 153
153
-
 154
154
-
 155
155
-
 156
156
-
 157
157
-
 158
158
-
 159
159
-
 160
160
본 자료는 10페이지 의 미리보기를 제공합니다. 이미지를 클릭하여 주세요.
-
1
-
2
-
3
-
4
-
5
-
6
-
7
-
8
-
9
-
10
-
11
-
12
-
13
-
14
-
15
-
16
-
17
-
18
-
19
-
20
-
21
-
22
-
23
-
24
-
25
-
26
-
27
-
28
-
29
-
30
-
31
-
32
-
33
-
34
-
35
-
36
-
37
-
38
-
39
-
40
-
41
-
42
-
43
-
44
-
45
-
46
-
47
-
48
-
49
-
50
-
51
-
52
-
53
-
54
-
55
-
56
-
57
-
58
-
59
-
60
-
61
-
62
-
63
-
64
-
65
-
66
-
67
-
68
-
69
-
70
-
71
-
72
-
73
-
74
-
75
-
76
-
77
-
78
-
79
-
80
-
81
-
82
-
83
-
84
-
85
-
86
-
87
-
88
-
89
-
90
-
91
-
92
-
93
-
94
-
95
-
96
-
97
-
98
-
99
-
100
-
101
-
102
-
103
-
104
-
105
-
106
-
107
-
108
-
109
-
110
-
111
-
112
-
113
-
114
-
115
-
116
-
117
-
118
-
119
-
120
-
121
-
122
-
123
-
124
-
125
-
126
-
127
-
128
-
129
-
130
-
131
-
132
-
133
-
134
-
135
-
136
-
137
-
138
-
139
-
140
-
141
-
142
-
143
-
144
-
145
-
146
-
147
-
148
-
149
-
150
-
151
-
152
-
153
-
154
-
155
-
156
-
157
-
158
-
159
-
160


목차
Ⅰ. 서 론
1. 연구의 필요성
2. 연구의 목적
3. 용어의 정의
Ⅱ. 문헌고찰
1. 건강행위에 관한 이론들
2. 근로자의 건강행위에 영향을 미치는 요인
3. 산업장 건강증진 프로그램의 참여에 영향을 미치는 요인
4. 산업장 건강증진 프로그램 사례
5. 산업장 건강증진 프로그램의 개발
Ⅲ. 연구의 개념틀 및 가설
1. 연구의 개념틀
2. 가설
Ⅳ. 연구방법
1. 연구설계
2. 연구대상
1) 대상 산업장
2) 대상 근로자 …
3. 연구도구
4. 연구절차
5. 분석방법
Ⅴ. 연구결과
1. 대상자의 일반적 특성
1) 인구사회학적 특성
2) 건강수준 관련 특성
2. 근로자의 건강위험요인 실태
1) 흡연
2) 음주
3) 식습관
4) 체중
5) 운동
6) 수면시간
7) Breslow Index
8) 스트레스
3. 규범, 태도, 지지, 변화의도
4. 건강위험요인과 변화의도간의 상관관계
5. 건강행위 변화의도에 대한 중회귀분석
6. 대상자의 유형 분류
7. 산업장 건강증진 프로그램 개발의 실제
Ⅵ. 고찰
1. 연구의 의의
2. 조사결과에 대한 고찰
3. 연구의 제한점
Ⅶ. 결론 및 제언
1. 연구의 필요성
2. 연구의 목적
3. 용어의 정의
Ⅱ. 문헌고찰
1. 건강행위에 관한 이론들
2. 근로자의 건강행위에 영향을 미치는 요인
3. 산업장 건강증진 프로그램의 참여에 영향을 미치는 요인
4. 산업장 건강증진 프로그램 사례
5. 산업장 건강증진 프로그램의 개발
Ⅲ. 연구의 개념틀 및 가설
1. 연구의 개념틀
2. 가설
Ⅳ. 연구방법
1. 연구설계
2. 연구대상
1) 대상 산업장
2) 대상 근로자 …
3. 연구도구
4. 연구절차
5. 분석방법
Ⅴ. 연구결과
1. 대상자의 일반적 특성
1) 인구사회학적 특성
2) 건강수준 관련 특성
2. 근로자의 건강위험요인 실태
1) 흡연
2) 음주
3) 식습관
4) 체중
5) 운동
6) 수면시간
7) Breslow Index
8) 스트레스
3. 규범, 태도, 지지, 변화의도
4. 건강위험요인과 변화의도간의 상관관계
5. 건강행위 변화의도에 대한 중회귀분석
6. 대상자의 유형 분류
7. 산업장 건강증진 프로그램 개발의 실제
Ⅵ. 고찰
1. 연구의 의의
2. 조사결과에 대한 고찰
3. 연구의 제한점
Ⅶ. 결론 및 제언
본문내용
roach and replication, Nursing Research, 38(2):88-93.
Zavela KJ, Davis LG, Cottrell RR, Smith WE(1988). Do only the healthy intend to participate in worksite health promotion?, Health Education Quarterly, 15(3):25-267.
ABSTRACT
Planning Health Promotion
Program in Workplace
Kyeong Ja Chun
Department of Public Health
Graduate School of Seoul National University
Directed by Prof. Hwa Joong Kim
In recent years, interests in health promotion have been stimulated by the epidemiological transition from infectious to chronic diseases as leading causes of death, the aging of the population, rapidly escalating health care costs, and epidemiologic findings linking individual risk to morbidity and mortality. It is not surprising that the workplace has been targeted as a promising setting for health promotion. Rationales for the workplace as an advantageous site for the efficient delivery of health promotion include : the large amount of time spent there by the majority of the population, the economic and other incentives for employers to invest in employee health promotion, the opportunity to mobilize peer pressure to help employees make desirable changes in health habits, as well as increasing reports of implementation of risk factor reduction at the worksite and some reports of program success.
In Korea, national attention to the opportunities for workplace health promotion began in the first 1990s. But there is no depth study to identify the relating factors to the health promotion program in the workplace.
The objective of this study is to find behavioral and physical characteristics that increase the person's risk for a range of health problems and to analysis other characteristics
to influence the degree of his/her intention to change health behavior. In addition, this study is purposed to present the process of planning health promotion program in the workplace.
To accomplish these objectives, two workplaces were selected. And 580 employees in those workplaces were served as subjects for the study.
Major findings in this study are as follows.
(1) They have many risk factors such as smoking, drinking, lack of sleeping time, law rate of regular exercise, irregular eating, stress.
(2) Some of the health risk factors such as smoking, drinking, and stress have the negative correlation to the intention to change.
(3) Among cognitive and socio-environmental factors, significant predictors to the intention are attitude to quit smoking and regular exercise, and social support including family support and interpersonal relationship.
(4) In the cluster analysis to segment the target population in to homogeneous unit, three clusters of lifestyle are specified in 'Kap Hoesa' and five clusters in 'Eul Hoesa'.
(5) In the case of 'Kap Hoesa', smoking cessation and exercise program are planned for risk group to change their behavior. In the case of 'Eul Hoesa', the stratege to raise the consciousness is suggested.
Key word : workplace, health promotion
Zavela KJ, Davis LG, Cottrell RR, Smith WE(1988). Do only the healthy intend to participate in worksite health promotion?, Health Education Quarterly, 15(3):25-267.
ABSTRACT
Planning Health Promotion
Program in Workplace
Kyeong Ja Chun
Department of Public Health
Graduate School of Seoul National University
Directed by Prof. Hwa Joong Kim
In recent years, interests in health promotion have been stimulated by the epidemiological transition from infectious to chronic diseases as leading causes of death, the aging of the population, rapidly escalating health care costs, and epidemiologic findings linking individual risk to morbidity and mortality. It is not surprising that the workplace has been targeted as a promising setting for health promotion. Rationales for the workplace as an advantageous site for the efficient delivery of health promotion include : the large amount of time spent there by the majority of the population, the economic and other incentives for employers to invest in employee health promotion, the opportunity to mobilize peer pressure to help employees make desirable changes in health habits, as well as increasing reports of implementation of risk factor reduction at the worksite and some reports of program success.
In Korea, national attention to the opportunities for workplace health promotion began in the first 1990s. But there is no depth study to identify the relating factors to the health promotion program in the workplace.
The objective of this study is to find behavioral and physical characteristics that increase the person's risk for a range of health problems and to analysis other characteristics
to influence the degree of his/her intention to change health behavior. In addition, this study is purposed to present the process of planning health promotion program in the workplace.
To accomplish these objectives, two workplaces were selected. And 580 employees in those workplaces were served as subjects for the study.
Major findings in this study are as follows.
(1) They have many risk factors such as smoking, drinking, lack of sleeping time, law rate of regular exercise, irregular eating, stress.
(2) Some of the health risk factors such as smoking, drinking, and stress have the negative correlation to the intention to change.
(3) Among cognitive and socio-environmental factors, significant predictors to the intention are attitude to quit smoking and regular exercise, and social support including family support and interpersonal relationship.
(4) In the cluster analysis to segment the target population in to homogeneous unit, three clusters of lifestyle are specified in 'Kap Hoesa' and five clusters in 'Eul Hoesa'.
(5) In the case of 'Kap Hoesa', smoking cessation and exercise program are planned for risk group to change their behavior. In the case of 'Eul Hoesa', the stratege to raise the consciousness is suggested.
Key word : workplace, health promotion
키워드
추천자료
 대도시 사무직 근로자의 건강관리행위의 관련요인 및 실천도에 관한 연구
대도시 사무직 근로자의 건강관리행위의 관련요인 및 실천도에 관한 연구 [건강증진론]우리나라 국민건강증진종합계획(Health Plan 2010)의 개요를 목표, 추진전략 및 ...
[건강증진론]우리나라 국민건강증진종합계획(Health Plan 2010)의 개요를 목표, 추진전략 및 ... 바람직한 건강행위
바람직한 건강행위 [환경보건학연구방법]보건행정 / 보건영양 / 건강증진 / 보건의식조사 / 기타 보건의료관리 ...
[환경보건학연구방법]보건행정 / 보건영양 / 건강증진 / 보건의식조사 / 기타 보건의료관리 ... 노인간호 및 노인수발보험에 대해 조사 및 노인 건강관리프로그램 계획서(A+레포트)
노인간호 및 노인수발보험에 대해 조사 및 노인 건강관리프로그램 계획서(A+레포트) 건강증진 관련 이론(건강신념모형, 건강증진모형, PRECEDE-PROCEED)
건강증진 관련 이론(건강신념모형, 건강증진모형, PRECEDE-PROCEED) [건강증진] 임부태아기 대상자의 건강증진
[건강증진] 임부태아기 대상자의 건강증진 건강행위변화이론 및 모형
건강행위변화이론 및 모형 건강증진론4B) 우리나라 국민건강증진종합계획 2020에서 금연사업의 세부영역 추진사업(예, ...
건강증진론4B) 우리나라 국민건강증진종합계획 2020에서 금연사업의 세부영역 추진사업(예, ... 2016년 2학기 건강증진론 중간시험과제물 B형(제4차 국민건강증진계획 노인건강)
2016년 2학기 건강증진론 중간시험과제물 B형(제4차 국민건강증진계획 노인건강) [간호학] 영아 건강증진을 위한 가족 중심 간호
[간호학] 영아 건강증진을 위한 가족 중심 간호 학령전기 아동과 가족의 건강증진
학령전기 아동과 가족의 건강증진