목차
1. 서 론
Ⅱ. 본 론
1. 한국과 러시아 관계의 회고
2. 양국간 사회․문화관계의 현황
(1) 인적교류
(2) 문화․예술교류
(3) 학술 및 과학기술 교류
Ⅲ. 결 론
참고문헌
표 차 례
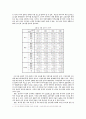
[표 1] 국별 입국자 추이
[표 2] 출국자 목적지 및 행선지별 추이
[표 3] 재러 한국유학생의 증감
[표 4] 한-러 지자체간 자매결연 현황
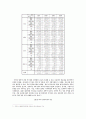
[표 5] 한국예술가 및 작가들의 (구)소련/러시아에서의 활동
[표 6] (구)소련/러시아 예술가 및 작가들의 한국에서의 활동
Ⅱ. 본 론
1. 한국과 러시아 관계의 회고
2. 양국간 사회․문화관계의 현황
(1) 인적교류
(2) 문화․예술교류
(3) 학술 및 과학기술 교류
Ⅲ. 결 론
참고문헌
표 차 례
[표 1] 국별 입국자 추이
[표 2] 출국자 목적지 및 행선지별 추이
[표 3] 재러 한국유학생의 증감
[표 4] 한-러 지자체간 자매결연 현황
[표 5] 한국예술가 및 작가들의 (구)소련/러시아에서의 활동
[표 6] (구)소련/러시아 예술가 및 작가들의 한국에서의 활동
본문내용
g on the social and cultural aspects. More than ten years have passed since the Soviet Union/Russia and the Republic of Korea estab- lished diplomatic relationship in 1990. The reestablished diplomatic relation- ship between the two countries allowed the non-official sector to increase the social and cultural relations in many aspects. So the article attempt to show how these aspects of socio-cultural relations between the two coun- tries have developed and what kind of problems impede the future devel- opment of the cooperation between them.
Overall review of the Korean-Russian relations show us that they had experienced two phases of development: the period of \"excessive excite- ment\" during the first several years and the period of \"rapidly cooling down\". Now they are entering the period of \"mutual management\". This kind of overall trend can be applied to understanding the Korean-Russian socio-cultural relations. However, in the field of cultural exchanges, two countries have developed most meaningful achievements. Although Russia took the role of \"supplier\" and Korea took the role of \"consumer\" of cul- tural contents at the first stage, recently they equally exchange programs in the cultural field. It means that the people of the two countries begin to estimate properly and understand each other.
However, the level of human exchanges is very low, comparing with other major countries. In the year of 2000, the number of visiting Korea Russians reached over 150 thousands (only 3% of the total visiting Korea foreigners) and the number of visiting Russia Koreans reached over 44 thousands (only 0.6% of the total visiting foreign countries Koreans). And the exchange of human resources and constructive cooperation at the regional level have increased, and this can be understood as a sign of consolidation of the relations between them. Besides, there are several signs of future development of the relations between them such as in- crease of cyber-communities concerning about Russia in Korea, information exchanges through internet, increasing number of Russian specialists in many fields acting in Korea and vise versa, etc.
Although the relationship between Korea and Russia has experienced ten years, we don\'t know the opposite sides quite well. In the period of mutual relations management, it is needed that we should endeavor after understanding each other, and prepare a mechanism and institutions for accumulating experiences about the opposite sides. For constructing more consolidated bases for the relations between Korea and Russia we should take not the viewpoint of simple calculation of benefits, but of complex understanding each other as a member of regional community. In this sense, we should underline that socio-cultural relations formally can be affected by the political and economic relations, but at the same time the socio-cultural relations between Korea and Russia can play a significant role in improving the whole relationship between them.
Overall review of the Korean-Russian relations show us that they had experienced two phases of development: the period of \"excessive excite- ment\" during the first several years and the period of \"rapidly cooling down\". Now they are entering the period of \"mutual management\". This kind of overall trend can be applied to understanding the Korean-Russian socio-cultural relations. However, in the field of cultural exchanges, two countries have developed most meaningful achievements. Although Russia took the role of \"supplier\" and Korea took the role of \"consumer\" of cul- tural contents at the first stage, recently they equally exchange programs in the cultural field. It means that the people of the two countries begin to estimate properly and understand each other.
However, the level of human exchanges is very low, comparing with other major countries. In the year of 2000, the number of visiting Korea Russians reached over 150 thousands (only 3% of the total visiting Korea foreigners) and the number of visiting Russia Koreans reached over 44 thousands (only 0.6% of the total visiting foreign countries Koreans). And the exchange of human resources and constructive cooperation at the regional level have increased, and this can be understood as a sign of consolidation of the relations between them. Besides, there are several signs of future development of the relations between them such as in- crease of cyber-communities concerning about Russia in Korea, information exchanges through internet, increasing number of Russian specialists in many fields acting in Korea and vise versa, etc.
Although the relationship between Korea and Russia has experienced ten years, we don\'t know the opposite sides quite well. In the period of mutual relations management, it is needed that we should endeavor after understanding each other, and prepare a mechanism and institutions for accumulating experiences about the opposite sides. For constructing more consolidated bases for the relations between Korea and Russia we should take not the viewpoint of simple calculation of benefits, but of complex understanding each other as a member of regional community. In this sense, we should underline that socio-cultural relations formally can be affected by the political and economic relations, but at the same time the socio-cultural relations between Korea and Russia can play a significant role in improving the whole relationship between them.











































소개글