-
1
-
2
-
3
-
4
-
5
-
6
-
7
-
8
-
9
-
10
-
11
-
12
-
13
-
14
-
15
-
16
-
17
-
18
-
19
-
20
-
21
-
22
-
23
-
24
-
25
-
26
-
27
-
28
-
29
-
30
-
31
-
32
-
33
-
34
-
35
-
36
-
37
-
38
-
39
-
40
-
41
-
42
-
43


목차
1. 근육의 구조
2. 근육의 수축
3. 근수축의 자극
4. 운동 단위
2. 근육의 수축
3. 근수축의 자극
4. 운동 단위
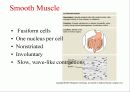
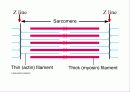
본문내용
Muscle Tissue
Skeletal Muscle
Cardiac Muscle
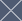
Smooth Muscle
Skeletal Muscle
Long cylindrical cells
Many nuclei per cell
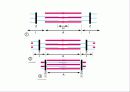
Striated
Voluntary
Rapid contractions
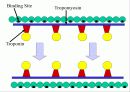
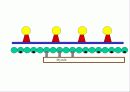
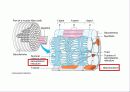
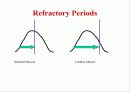
Skeletal muscle attaches to our skeleton. *The muscle cells a long and cylindrical. *Each muscle cell has many nuclei. *Skeletal muscle tissue is striated. It has tiny bands that run across the muscle cells. *Skeletal muscle is voluntary. We can move them when we want to. *Skeletal muscle is capable of rapid contractions. It is the most rapid of the muscle types.
Skeletal Muscle
Cardiac Muscle
Smooth Muscle
Skeletal Muscle
Long cylindrical cells
Many nuclei per cell
Striated
Voluntary
Rapid contractions
Skeletal muscle attaches to our skeleton. *The muscle cells a long and cylindrical. *Each muscle cell has many nuclei. *Skeletal muscle tissue is striated. It has tiny bands that run across the muscle cells. *Skeletal muscle is voluntary. We can move them when we want to. *Skeletal muscle is capable of rapid contractions. It is the most rapid of the muscle types.

























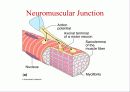
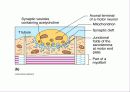

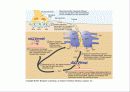



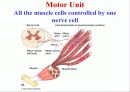



















소개글